What Data Types Are Biometric Data Stored In
What is biometrics?
Biometrics is the measurement and statistical analysis of people's unique concrete and behavioral characteristics. The engineering is mainly used for identification and admission command or for identifying individuals who are under surveillance. The basic premise of biometric authentication is that every person tin can be accurately identified by intrinsic physical or behavioral traits. The term biometrics is derived from the Greek words bio, meaning life, and metric, meaning to measure.
How do biometrics work?
Authentication by biometric verification is becoming increasingly common in corporate and public security systems, consumer electronics and bespeak-of-sale applications. In improver to security, the driving strength backside biometric verification has been convenience, as there are no passwords to remember or security tokens to carry. Some biometric methods, such as measuring a person'southward gait, tin can operate with no direct contact with the person beingness authenticated.
Components of biometric devices include the following:
- a reader or scanning device to record the biometric factor being authenticated;
- software to catechumen the scanned biometric data into a standardized digital format and to compare match points of the observed information with stored data; and
- a database to securely store biometric data for comparison.
Biometric data may be held in a centralized database, although modern biometric implementations oft depend instead on gathering biometric data locally and then cryptographically hashing information technology and then that hallmark or identification can be accomplished without direct access to the biometric information itself.
Types of biometrics
The 2 primary types of biometric identifiers are either physiological characteristics or behavioral characteristics.
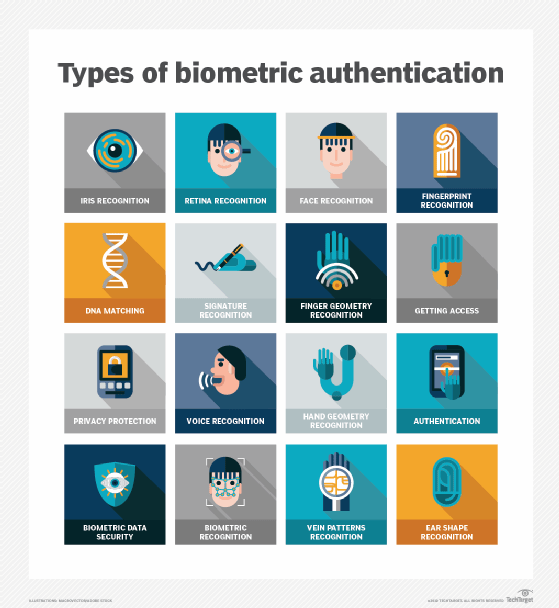
Physiological identifiers relate to the limerick of the user being authenticated and include the post-obit:
- facial recognition
- fingerprints
- finger geometry (the size and position of fingers)
- iris recognition
- vein recognition
- retina scanning
- voice recognition
- Dna (deoxyribonucleic acrid) matching
- digital signatures
Behavioral identifiers include the unique ways in which individuals act, including recognition of typing patterns, mouse and finger movements, website and social media engagement patterns, walking gait and other gestures. Some of these behavioral identifiers tin can be used to provide continuous authentication instead of a single ane-off authentication check. While it remains a newer method with lower reliability ratings, information technology has the potential to grow alongside other improvements in biometric engineering science.
Biometric data can be used to admission information on a device like a smartphone, but there are likewise other ways biometrics can be used. For example, biometric information can be held on a smart card, where a recognition system volition read an private'south biometric information, while comparing that confronting the biometric information on the smart card.
Advantages and disadvantages of biometrics
The use of biometrics has plenty of advantages and disadvantages regarding its utilize, security and other related functions. Biometrics are benign for the following reasons:
- hard to faux or steal, different passwords;
- easy and convenient to utilise;
- generally, the aforementioned over the course of a user's life;
- nontransferable; and
- efficient considering templates take up less storage.
Disadvantages, withal, include the following:
- Information technology is plush to become a biometric system up and running.
- If the system fails to capture all of the biometric data, it can lead to failure in identifying a user.
- Databases belongings biometric data can nevertheless be hacked.
- Errors such as false rejects and imitation accepts can still happen.
- If a user gets injured, then a biometric authentication system may non work -- for example, if a user burns their mitt, then a fingerprint scanner may not be able to identify them.
Examples of biometrics in utilize
Aside from biometrics being in many smartphones in utilise today, biometrics are used in many different fields. As an example, biometrics are used in the following fields and organizations:
- Law enforcement. It is used in systems for criminal IDs, such every bit fingerprint or palm print authentication systems.
- U.s. Department of Homeland Security. Information technology is used in Border Patrol branches for numerous detection, vetting and credentialing processes -- for example, with systems for electronic passports, which store fingerprint data, or in facial recognition systems.
- Healthcare. It is used in systems such every bit national identity cards for ID and health insurance programs, which may use fingerprints for identification.
- Airport security. This field sometimes uses biometrics such as iris recognition.
However, not all organizations and programs will opt in to using biometrics. As an example, some justice systems volition not use biometrics so they can avoid whatsoever possible error that may occur.
What are security and privacy bug of biometrics?
Biometric identifiers depend on the uniqueness of the factor being considered. For example, fingerprints are generally considered to be highly unique to each person. Fingerprint recognition, specially as implemented in Apple's Touch ID for previous iPhones, was the first widely used mass-market application of a biometric hallmark cistron.
Other biometric factors include retina, iris recognition, vein and voice scans. However, they take not been adopted widely then far, in some part, because in that location is less confidence in the uniqueness of the identifiers or considering the factors are easier to spoof and apply for malicious reasons, like identity theft.
Stability of the biometric factor can as well be important to credence of the cistron. Fingerprints practice not alter over a lifetime, while facial appearance can alter drastically with age, disease or other factors.
The well-nigh meaning privacy issue of using biometrics is that physical attributes, like fingerprints and retinal blood vessel patterns, are generally static and cannot be modified. This is distinct from nonbiometric factors, like passwords (something one knows) and tokens (something one has), which tin exist replaced if they are breached or otherwise compromised. A demonstration of this difficulty was the over 20 million individuals whose fingerprints were compromised in the 2014 U.S. Office of Personnel Management data breach.
The increasing ubiquity of high-quality cameras, microphones and fingerprint readers in many of today's mobile devices ways biometrics will continue to go a more common method for authenticating users, particularly as Fast ID Online has specified new standards for authentication with biometrics that support two-factor authentication with biometric factors.
While the quality of biometric readers continues to improve, they tin can still produce false negatives, when an authorized user is not recognized or authenticated, and false positives, when an unauthorized user is recognized and authenticated.
Are biometrics secure?
While high-quality cameras and other sensors assistance enable the apply of biometrics, they can besides enable attackers. Because people practise not shield their faces, ears, hands, voice or gait, attacks are possible only by capturing biometric information from people without their consent or knowledge.
An early attack on fingerprint biometric authentication was chosen the sticky bear hack, and it dates dorsum to 2002 when Japanese researchers, using a gelatin-based confection, showed that an assailant could lift a latent fingerprint from a sleeky surface. The capacitance of gelatin is similar to that of a human finger, so fingerprint scanners designed to observe capacitance would be fooled by the gelatin transfer.
Adamant attackers can also defeat other biometric factors. In 2015, Jan Krissler, also known as Starbug, a Chaos Computer Club biometric researcher, demonstrated a method for extracting enough data from a high-resolution photograph to defeat iris scanning hallmark. In 2017, Krissler reported defeating the iris scanner authentication scheme used past the Samsung Milky way S8 smartphone. Krissler had previously recreated a user's thumbprint from a high-resolution paradigm to demonstrate that Apple's Touch ID fingerprinting authentication scheme was also vulnerable.
Later Apple released iPhone X, it took researchers merely two weeks to bypass Apple tree's Face ID facial recognition using a 3D-printed mask; Face ID tin can also be defeated by individuals related to the authenticated user, including children or siblings.
This was concluding updated in July 2021
Go along Reading Well-nigh biometrics
- Biometric IoT sensors shape the future of user interfaces
- IoT biometrics play a greater role in workplaces
- In biometrics, security concerns span technical, legal and upstanding
- Biometric hallmark terms to know
- Dangers of biometric hallmark for mobile devices
Dig Deeper on Identity and admission management
-

biometric payment
-

What is biometric authentication?
-

Microsoft Windows How-do-you-do
-
![]()
Biometric security engineering could run across growth in 2021
What Data Types Are Biometric Data Stored In,
Source: https://www.techtarget.com/searchsecurity/definition/biometrics
Posted by: mastersnountylegrel.blogspot.com






0 Response to "What Data Types Are Biometric Data Stored In"
Post a Comment